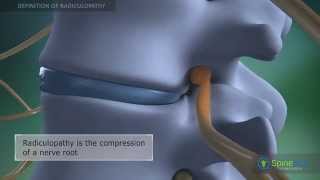
Radiculopathy
Thoracic Radiculopathy - Definition, Causes, Risk Factors and Complications
Radiculopathy: What is Thoracic Radiculopathy?
Thoracic Radiculopathy is used to describe a variety of sensations (mostly pain) that originates from the middle portion of a person’s spine. The name Thoracic Radiculopathy itself is made up of two words.
The word radiculopathy refers to a variety of symptoms that include radiating pain, tingling sensation, as well as numbness and weakness in the area affected by the condition.
The word thoracic refers to the center part of your spine, which is composed of 12 vertebrae known as the thoracic vertebrae.
The most common type of radiculopathy is Lumbar Radiculopathy, which refers to a variety of sensations (same as thoracic radiculopathy) that comes from the lower back part of the spine. Another more common type of radiculopathy is Cervical Radiculopathy this time originating from the neck. Compared to these two types of radiculopathy, Thoracic Radiculopathy is very rare.
What are the most common causes of Thoracic Radiculopathy?
Thoracic Radiculopathy can be caused by a variety of other factors, but the some of the more common conditions that might cause Thoracic Radiculopathy are the following:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Any disease concerning the spine, especially those associated with the aging changes in our body, can be a primary cause of radiculopathy.
- Bulging Disc: as mentioned before, any degenerative condition that involves the spine can be a potential cause of a person’s capacity to experience the condition known as Thoracic Radiculopathy.
- Spinal Injury: Having a history of spinal injury or any injury that is in the immediate area near your spine can be a major cause of Thoracic Radiculopathy as this condition speeds up the degeneration and can cause all sorts of conditions involving the spine.
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is also another spine or vertebra-related condition that may be a leading cause of Thoracic Radiculopathy. This is because osteoarthritis is the degeneration of the spine, and any condition that affects the spine puts a person at a bigger risk of developing Thoracic Radiculopathy, or any other radiculopathy for that matter.
- Herniated Disc
- Bone spurs
- Diabetes- especially in older patients
- Spinal Stenosis
- Foraminal Stenosis
What are some Risk Factors you should look out for in Thoracic Radiculopathy?
The most common factor that puts a person at risk for developing Thoracic Radiculopathy is the repetitive bearing of excessive load on the spine. Whether it is part of a person’s job or a sport that a person is involved in, when that activity places a burden on your spine and does it repetitively, then it can put the person at risk of having Thoracic Radiculopathy.
If you also have a family history of radiculopathy or any other degenerative or problematic spinal conditions, then you are at risk of developing Thoracic Radiculopathy
Complications involving Thoracic Radiculopathy
Some of the complications that could develop if you have radiculopathy are the following:
- Neurologic Deficits (Spinal) - Since the problem involves the spinal column where most of our nerves connect towards the nervous systems in our brain, Neurological problems are not all that surprising to develop when a person has Thoracic Radiculopathy.
- Bowel and Bladder Incontinence -As the case with most problems and complications involving spinal disorders, bowel, and bladder incontinence may develop as a result of Thoracic Radiculopathy. A person will develop problems holding his/her bowel and bladder in.
- Chronic Back Pain -Chronic Back Pain can also develop as a result of Thoracic Radiculopathy, is especially felt in the middle back area of the person affected, and may become chronic if not treated initially.
- Problems performing everyday tasks and work - Because your basic functions are affected by the condition, a valid complication will be difficulty in having you perform everyday tasks that you were routinely doing before developing the condition.
Top Thoracic Radiculopathy Symptoms and Diagnostic Procedures Used
What are the most common radiculopathy symptoms that may manifest in a person?
Since Thoracic Radiculopathy is a condition in which the nerves in your spinal column are affected, there are many Thoracic Radiculopathy symptoms that vary greatly from which nerves are affected. The most commonly associated body parts in Thoracic Radiculopathy are the muscles of the chest and the abdomen, as well as the surrounding areas around it.
Some of the most commonly associated signs and Thoracic Radiculopathy symptoms include:
- Pain in the affected area: The most common of Thoracic Radiculopathy symptoms is perhaps the pain it causes and its location. In Thoracic Radiculopathy, where the pain is felt differs largely from other types of radiculopathy, as it can be felt in the middle area of the back, in comparison to the neck area (cervical) or lower area (lumbar). The pain may also radiate towards the chest and torso as well as in the immediate area surrounding the middle of the back.
- Numbness in the affected area: along with the pain, numbness is also felt in the area affected by Thoracic Radiculopathy symptoms. The numbness can primarily be felt in the middle area of your back, but can also radiate towards the neighboring parts as well as in the chest and torso of the person affected.
- Tingling: there is also a tingling sensation to be felt in the area affected (middle area of the back) as well as in the immediate area surrounding it. The tingling sensation can also be felt in the upper body and chest of the person affected.
Thoracic Radiculopathy is often mistaken for shingles, as the sharp stabbing pain that is felt in the chest and upper body areas is also a symptom of an early onset of shingles without any blisters or rashes present.
What are the Medical Procedures that can be used by doctors to Diagnose Thoracic Radiculopathy?
When it comes to thoracic syndromes, there is a broad spectrum of different diagnosis, making it hard for physicians to discover the cause or difference between other thoracic diseases. Nevertheless, a differentiation between Thoracic Radiculopathy and other thoracic conditions is important, in order to accurately remedy and treat the condition.
These are some of the diagnostic medical procedures your physician may explore to determine if you indeed have Thoracic Radiculopathy:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Of course, any diagnosis conducted by a general physician always begins with the reviewing and evaluation of your previous medical history as a physical examination. In the medical history part, the doctor will subject you to various questions to determine where the condition is originating and what might its cause be based on your situation. The physical examination, on the other hand, will focus on your physical capacity to assess the severity of the situation, such as muscle strength of the affected area, as well as the sensation around it and your reflexes.
- Imaging Tests: Another option is conducting imaging tests such as Plain Radiographs, X-ray, MRI, Myelography or CT Scan to accurately determine the source of the condition. This is also done to determine if the pain you are feeling may be caused by another underlying condition such as trauma, and osteoarthritis.
- Electrodiagnostic Evaluation: this process involves performing all of these other medicals procedures such as Needle EMG of abdominal, intercostals and thoracic paraspinal muscles. This diagnostic procedure can also be useful in identifying if the condition is diabetic Thoracic Radiculopathy in comparison to other intrathoracic and intraabdominal diseases.
- Diagnostic Selective Nerve Root Block: this type of diagnostic procedure can also be used to confirm your Thoracic Radiculopathy symptoms. This procedure is done by excluding pain generators around your thoracic area to accurately determine what part of your body is emitting the pain and therefore has problems that need to be treated.
Thoracic Radiculopathy: Treatment for Radiculopathy and Prevention
What is the most common treatment for radiculopathy in use today?
There is a wide variety of treatments available for people who are experiencing radiculopathy, and one prescribed treatment for radiculopathy may vary from one physician to the other. Nevertheless, it is important to know what kinds of treatment for radiculopathy is made available to you so you can choose the one that’s best suited for you and your overall health.
Conservative Treatment
However, most of the time, the treatment for radiculopathy currently is through the use of conservative treatment. Conservative treatment for radiculopathy may involve the use of:
- Anti-inflammatory meds: Medications that contain anti-inflammatory properties, as well as painkilling properties, are an ideal conservative treatment for radiculopathy and the people who are experiencing the condition. Anti-inflammatory medications may include NSAIDs or Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs such as Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen, and Naproxen Sodium.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can also be prescribed by your physician, although this treatment for radiculopathy is often prescribed hand in hand with other conservative treatments such as the one mentioned above. This is done in order to ensure fast and effective recovery.
- Chiropractic Treatment: this type of treatment for radiculopathy may also be prescribed by your doctor along with those conservative treatments mentioned above. You will be referred by your physician to a licensed chiropractor in this case.
- Avoiding Heavy Work: Another conservative treatment is by simply avoiding doing heavy active work, especially those that can strain the neck and back.
In most cases encountered by physicians, the patients affected with radiculopathy that undergoes this type of conservative treatment usually respond well, and their situations and conditions improve in as fast as 6 weeks, up to 3 months.
Epidural Steroid Injection
In the case that the patient doesn’t respond well to the conservative treatment efforts mentioned above, the patient may then be prescribed with an epidural steroid injection.
This procedure is done with the assistance of an x-ray machine, and then the doctor then proceeds to inject steroid medication in the spine, specifically in the bones between them, adjacent to the nerves that are affected. Epidural steroid injections have been proven to help reduce inflammation and irritation fast and may help to reduce some of the other symptoms of the condition.
Surgery
As with most bone related illnesses and conditions, surgery is always available as an option, although as the last option. Surgery is reserved for people whose thoracic radiculopathy symptoms continue to persist even after being subjected to all of the treatments mentioned above.
The goal of the surgery, in this case, is the removal of the compression of the nerves that are affected by the condition. There are two types of surgery that can be chosen from but are largely dependent on what is the cause of your thoracic radiculopathy. The two types of surgery to treat Thoracic Radiculopathy are:
- Laminectomy: the surgical procedure of laminectomy seeks to remove only a small portion of the bone in your spinal cord that is covering or compressing the nerve. This is done so that the nerve has an additional space and will not be compressed.
- Discectomy: the surgical procedure of discectomy, on the other hand, seeks to remove the portion of the disc that is already herniated and is compressing the nerve that is affected.
Generally, surgery, especially open surgery is avoided because of the many high-risk complications it presents. Surgery is used by physicians whenever less invasive and conservative treatments for thoracic radiculopathy fail at doing the job.
Thoracic Radiculopathy Prevention
Although there are no proven methods to prevent radiculopathy, there are certain strategies you may take to decrease your risk of having the condition:
- You must maintain good posture, even when sitting or doing sedentary activities such as driving and sitting in front of a computer
- Proper technique and posture when lifting
- Conditioning the muscles by doing regular physical activities
- Incorporating stretching into exercise routines and doing warm-ups.






